Meaning
Mergers and acquisitions or (M&A) is the process of combining two separate companies into one.
Merger means when two firms of approximately same size, who join forces to form a single new entity. It is also called “merger of equals”. The terms of the merger are often fairly friendly and mutually agreed by owners of two different company to become equal partners in the new venture.
Acquisition means when one company takes over other company, and establishes itself as the new owner of the newly formed company either through purchasing shares or acquiring assets. The target company agrees to exit, the buyer absorbs the company.
The end result of both process is same but the relationship between the two companies’ owner differs based on the agreement they signed on.
The only difference between Merger and Acquisition is that in merger, both the companies are of same size. But in an acquisition, the buyer is always bigger than the seller.
Why companies choose Mergers or Acquisition?
The reason behind merger or acquisition agreement is that companies can together create more value compared to being on an individual stand. With the goal of wealth maximization, companies keep evaluating opportunities for merging with other company or acquiring the whole company.
Stages involved in M&A
Investment bankers’ advice their clients on various M&A steps to be followed.
1) Developing Acquisition Strategy
This step revolves around the acquirer having a clear idea of what they expect to gain from this strategy. What their purpose is for acquiring the target company (e.g. to expand the product lines or to gain access to new market).
2) Setting M&A Search Criteria
Determining the criteria for identifying target companies (e.g. profit margin, location of business, its target audience).
3) Searching Potential Acquisition Targets
Acquirer then evaluate potential target companies based on its search criteria.
4) Begin planning for Acquisition
Acquirer then contact one or more companies that meet its search criteria and offer them good value. The purpose of this conversation is to verify more information about the inside of the company and to see how willing the owner is with an idea of merger or acquisition strategy.
5) Performing Valuation Analysis
If the conversation goes well, acquirer ask the target company to provide some important business data (current financial accounts, audit report, sales report, etc.) that will help the acquirer to further evaluate more about the business and its owner.
6) Negotiations
After analyzing the company’s data, the acquirer should decide a reasonable offer. Once the offer is kept in front of the target owner, both companies can negotiate terms in more detail.
7) M&A Due Diligence
Due diligence is the process that begins when the offer has been accepted by the target company. It aims to confirm the acquirer assessment of the value of the target company by properly examining the company’s operational reports (current financial accounts, audit report, sales report, etc.)
8) Purchase and Sales contract
After completing due diligence process, next step is to execute a final contract; the parties make a final decision on the type of purchase agreement, whether it should be asset purchase or share purchase.
9) Financing Strategy for the Acquisition
Companies have already decided the payment options for the deal earlier, but the details of payment will come together after signing the purchase and sales contract. Thus a separate form will be signed by the two parties agreeing the mode of payment.
10) Closing of the Acquisition
The acquisition deal closes, later the management teams of both companies work together on the process of merging the two businesses.
Advantages of M&A
1) Increase in Market Share
If both the companies are of the same industry, combining the resources of both companies may result in larger market share.
2) Increase in distribution capabilities
By expanding geographically, companies can add to their distribution network or expand its service area.
3) Increase in Labor
Expanding the company also benefits of getting more labor, thus more production which leads to growth and development.
4) Enchased Financial Resources
The financial statement of both combined companies is generally greater than the stand-alone company, this make new investment possible.
Disadvantages of M&A
1) Large expenses is associated buying a company
If the target owner doesn’t want its company to be acquire. Acquirer has to offer him a higher value to make him agree for their contract.
2) A clash in a business relation
If acquirer tries to forcefully convince the target owner for the M&A decision, it will put negative impact on the business relation between both parties.
3) Key staff isn’t interested to join a new company
Sometimes a staff doesn’t want to work with the new company based on its likes and preferences.
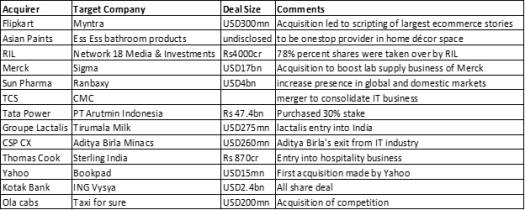
Recent Mergers and Acquisitions
References
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/mergersandacquisitions.asp
- https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/021815/what-difference-between-merger-and-acquisition.asp
- https://www.edupristine.com/blog/mergers-acquisitions
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/deals/mergers-acquisitions-ma/
- https://www.shopify.in/encyclopedia/mergers-and-acquisitions-m-a
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/allbusiness/2018/08/27/mergers-and-acquisitions-key-considerations-when-selling-your-company/
- https://debitoor.com/dictionary/mergers-and-acquisitions
- https://efinancemanagement.com/mergers-and-acquisitions
- https://www.ansarada.com/mergers-acquisitions
- https://www.educba.com/what-is-mergers-and-acquisitions/